|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Have you ever used a website or app that was frustrating to navigate or didn’t meet your needs? That’s where UX design comes in. But what exactly is UX design?
User experience (UX) design is a crucial aspect of creating successful digital products. It involves understanding the needs and behaviours of users and designing interfaces and interactions that are intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable to use.
In this article, we’ll explore what UX design is, why it’s important, and how it differs from other design disciplines.
UX Design
UX design, or user experience design, is the process of creating meaningful and seamless interactions between users and a digital product or service to enhance usability, satisfaction, and overall user engagement.
What is User experience (UX) Design?
User experience (UX) design is a crucial component of modern-day product and service development. At its core, UX design is about creating positive experiences for users across all touchpoints of a product or service. This includes the way users interact with a product, how it makes them feel, and how easily they can achieve their goals.
Whether it’s the physical feel of a product in a user’s hand or the simplicity of a checkout process when buying online, every element of a user’s experience matters. The objective of UX design is to deliver an effortless, effective, relevant, and enjoyable experience for the user.
UX design is a multidisciplinary field that combines market research, product development, strategy, and design to craft user experiences that are intuitive, seamless, and engaging. The UX designer’s role is to build a bridge between the customer and the company, ensuring that the user’s needs and expectations are met with every interaction.
In essence, user experience is about creating meaningful, memorable experiences that users will want to come back to. Whether it’s a website, mobile app, or physical product, the principles of UX design can be applied to any product or service.
By focusing on the user, UX designers help companies create products that meet real customer needs and drive business success.
The difference between UX and UI Design
As technology continues to advance, the importance of user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design in creating successful digital products cannot be overstated. Despite often being used interchangeably, it’s crucial to recognize that UX and UI are two different things.
UI design refers to the actual interface of a product, encompassing everything from visual design to the interactive elements of a product’s interface. It covers elements such as typography, colour palettes, animations, and navigational touchpoints like buttons and scrollbars.
In contrast, UX design focuses on the user’s journey to solve a problem. It’s concerned with how users interact with a product, their overall satisfaction, and how well it meets their needs.
As Ken Norton, Partner at Google Ventures, and former Product Manager at Google states, “UX is focused on the user’s journey to solve a problem; UI is focused on how a product’s surfaces look and function.”
It’s essential to note that while UX and UI design are different, they work hand in hand to create a successful product. The design of a product’s interface has a significant impact on the overall user experience. Therefore, designers must pay close attention to both UX and UI design elements to create an optimal user experience.
UX design can be found everywhere, from the layout of a supermarket to the ergonomics of a vehicle, and the usability of a mobile app. As digital products continue to evolve, the importance of UX and UI design will continue to play a vital role in creating products that delight and engage users.
4 key Principles of UX Design
User experience (UX) design can sometimes seem elusive and difficult to define. As a discipline that revolves around the user and their goals, what constitutes good UX can vary significantly depending on the product and user base.
Nonetheless, at its core, good UX design is about creating experiences that solve user needs most seamlessly and enjoyably as possible.
To achieve this, four key principles underpin effective UX design:
1. The user comes first (always)
The fundamental principle of UX design is that the user always comes first. While this may seem self-evident, it’s worth emphasizing given the many competing priorities and pressures that product teams often face.
Good UX design places the user’s needs at the heart of every decision. The product should be optimized to help users reach their goals or solve their problems in the quickest, easiest way possible. All aspects of the design, from the initial concept to the final feature, should flow from this core principle.
Adhering to user-centred design principles can provide a significant competitive advantage for companies that get it right. However, putting users first is not always easy, particularly when business goals and objectives come into play. The challenge is to ensure that business goals align with user needs and work to support them, rather than undermine them.
Recipe websites offer a great example of how businesses can put users first. While lengthy blog posts can help these websites rank higher in search engines, they can also obstruct users from accessing the content they’re interested in – the recipe itself. To address this, some sites have added a ‘Jump to Recipe’ button, enabling users to quickly navigate to the content they’re seeking.
Ultimately, designing with the user in mind is crucial for creating positive user experiences that meet and exceed user expectations. By consistently prioritizing user needs and goals, businesses can drive greater user engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty, leading to long-term success.
2. Simplicity, hierarchy, and consistency
When it comes to good UX design, simplicity, hierarchy, and consistency are key principles that work together closely. Simple, hierarchical, and consistent design helps users quickly find what they need and accomplish their goals with ease.
Simplicity does not mean sacrificing function, but rather focusing on eliminating unnecessary visual clutter and steps that can complicate the user experience. By simplifying design, users can navigate more efficiently and effectively. A clear hierarchy in design helps users understand the structure of the product and find what they need without any confusion.
Consistency is also critical for good UX design. Consistent branding, marketing, and support help unify the user experience. Apple’s App Store is an excellent example of consistency. Users can seamlessly switch between devices, and the user experience remains consistent, with similar gestures, icons, hierarchy, and visual style across all devices.
By adhering to the principles of simplicity, hierarchy, and consistency, you can create a user-centred design that empowers users to accomplish their goals with ease. These principles can help streamline the user experience and make it a pleasure to use your product.
3. Functionality first, then design
In the world of UX design, the functionality should always take precedence over design. While UI (user interface) focuses on the aesthetics of a product, UX (user experience) is concerned with how the product functions.
The ultimate goal of good UX design is to make it as effortless as possible for users to achieve their desired tasks on your site or app, and this requires prioritizing clarity and function.
The design should never impede or slow down users but rather should enhance the user experience. One common mistake is to place too much emphasis on visual aesthetics at the expense of functionality. This can be seen in Moleskine’s iOS calendar app, Timepage, where users can choose colour themes. While the UI looks sleek and stylish, the design makes it harder for users to view their options and select the colour they want.
When designing a product, it’s important to start with the basics of its function and build it up from there. By focusing on the core functionality, designers can ensure that users can easily accomplish their goals without distractions or obstacles.
Once the functionality has been established, designers can then work on improving the product’s aesthetics and creating a design that enhances the user experience.
4. Draw on the familiar
When designing UX, it’s crucial to draw on familiar elements and interactions that make sense for users. By leveraging design frameworks and patterns that users are already familiar with, we can create a more intuitive experience that users find easy to understand and use.
Designing interactions that aren’t familiar to users can create a learning curve and add barriers that make it harder for users to accomplish their goals. On the other hand, drawing on familiar elements and interactions can lead to a smoother user experience and help users achieve their objectives more easily.
For example, iPhone users are accustomed to swiping right and left, so building that familiar interaction into your product’s design can enhance the UX. That’s why many iPhone apps, including Tinder, utilize this gesture. It’s what users expect, and integrating it into your design can ensure users have an easier time using your product.
Overall, drawing on the familiar is an essential principle of UX design. By using familiar elements and interactions, we can create an experience that feels intuitive, natural, and easy to use, helping users achieve their goals and creating a positive impression of our products.
Why is UX design important for product teams?
UX design is a critical component of product development that can make or break the success of a product. When users struggle to navigate a product, experience bugs or encounter issues that create friction, they are likely to churn. By prioritizing UX design as a core part of the development process, product teams can reduce churn and improve customer satisfaction.
Investing in the user experience helps create a valuable product that effectively solves users’ problems and helps them reach their goals. By leveraging UX design, product teams can convert more users, drive adoption, boost customer retention, and increase loyalty.
A positive user experience can also be a competitive advantage, allowing companies to differentiate themselves in crowded markets. Products that prioritize simplicity, hierarchy, consistency, and familiar interactions are more likely to resonate with users, increasing the likelihood of adoption and retention.
In short, UX design is essential for product teams because it enables them to create products that meet users’ needs and exceed their expectations. By prioritizing the user experience, product teams can create a competitive advantage and foster long-term customer loyalty.
Investing in UX design can lead to a valuable product that effectively addresses user problems and assists in achieving their objectives. The product team can use UX design to:
- Convert more users
- Drive Adoption
- Boost customer retention and loyalty
- Banish churn
The Design Thinking Process
The Design Thinking Process is an essential tool for UX designers, helping them to create user-centred products that meet the needs and expectations of their target audience.
This process can be broken down into four stages: inspiration, conceptualization, iteration, and exposition.
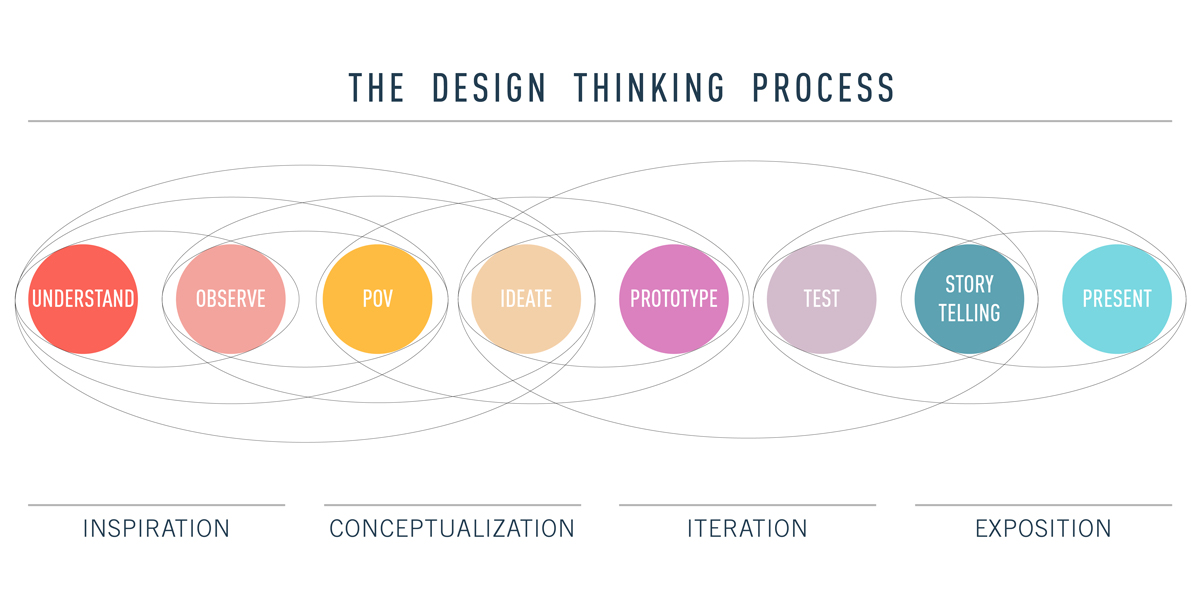
During the inspiration stage, the UX designer conducts extensive research and competitor analysis to fully understand the problem or challenge they are setting out to solve. This involves interviewing users and other stakeholders to identify their goals, emotions, pain points, and behaviours, which are used to create user personas. The designer also considers information architecture and maps out user flows.
In the conceptualization stage, the designer visually brainstorms solutions for each step in the user flow, creating wireframes and prototypes of what the final product might look like. This is a crucial step as it helps the designer identify potential issues with the product’s design and functionality.
During the iteration stage, the UX designer conducts usability tests to see how users interact with the product. This feedback allows them to identify any issues or obstacles that users may encounter while using the product and make changes accordingly.
Finally, during the exposition stage, the UX designer presents their ideas and designs to key stakeholders, such as product managers and developers, to ensure that everyone is aligned on the project’s goals and vision.
By following the Design Thinking Process, UX designers can create products that are not only functional and easy to use but also provide a positive user experience. This, in turn, can lead to increased user engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty, making it a critical tool for any product team.
Company size determines the scope of what a UX designer does
The UX design process can vary depending on the size and specific needs of a company. In larger companies, the UX design team may consist of multiple designers, each focusing on a specific aspect of the process such as research or visual design. These designers work together to ensure the product meets the needs of the end users.
On the other hand, smaller companies and startups often have a limited number of team members. In this case, the UX designer is likely to wear many hats and take on a variety of tasks, including user research, prototyping, and visual design. This may require the designer to be versatile and able to adapt to changing priorities and requirements.
Regardless of the size of the company, UX designers play a crucial role in the success of the product.
They ensure that the user’s needs are met and that the product is easy and enjoyable to use. This, in turn, can lead to increased customer satisfaction, better retention rates, and higher conversions.
Key questions UX designers ask themselves
As UX designers work through the design process, they consistently ask themselves a set of key questions to ensure the success of the product. These questions include:
- Is the product usable? Is it logical, self-explanatory, and easy to use?
- Does the product or service solve an existing user problem?
- Is it accessible to different categories of users? You can read more about accessibility in design further on.
- Is the product or service desirable? Does it create a positive experience that the user would be happy to repeat?
- Learn more: What Does a UX Designer Do?
What kinds of projects do UX designers work on?
The field of UX design is vast and ever-expanding, with professionals finding themselves working on a wide range of projects in various contexts. As the tech industry continues to grow and evolve, so too does the scope of what a UX designer can work on.
Here are just a few examples of the kinds of projects that UX designers might be involved in:
Website, app, and software design
As technology continues to advance, the role of UX design is expanding to encompass a wide range of projects across various contexts. One of the most common applications of UX design is a website, app, and software design. In today’s digital age, the usability of a website, mobile app, or software is crucial to its success in the market.
UX designers, in collaboration with UI designers, play a vital role in ensuring a smooth online experience for users. They conduct user research to understand the needs, preferences, and behaviours of target users. Based on this research, they create wireframes, prototypes, and designs that are intuitive, user-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing.
From e-commerce websites to dating apps, from customer relationship management (CRM) software to web-based email clients, every online journey that users take has been meticulously crafted by a team of UX professionals.
By designing seamless and engaging digital experiences, UX designers help businesses to attract and retain customers, increase sales and revenue, and establish a strong online presence.
Voice design
The rise of voice user interfaces (VUI) is changing the way we interact with technology, and UX designers are at the forefront of this transformation.
As more people turn to voice search, VUI design has become an essential aspect of UX design. In the U.S. alone, almost 50% of adults use voice search daily.
UX designers play a vital role in the success of VUI products like Amazon Alexa by ensuring they are user-friendly and accessible to a wide range of people. However, designing for voice requires a different approach than designing for websites and apps. It requires an understanding of how people naturally speak and interact with technology.
Designers working in VUI must think about how the user’s spoken commands will be interpreted, and how the system will respond. They must consider the context in which users are speaking, and design for a range of accents, languages, and speech patterns.
Despite its unique challenges, VUI design provides exciting opportunities for UX designers to create innovative products and services that are more accessible and user-friendly than ever before.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR)
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are rapidly growing fields in the tech industry. The global VR market is expected to reach $44.7 billion by 2024, and augmented reality has already made a significant impact on the Pokemon Go craze.
As a result, UX designers are increasingly being called upon to design immersive experiences in these emerging technologies.
Designing for VR and AR presents unique challenges, as the user experience is not limited to a traditional screen or interface. UX designers must consider factors such as spatial awareness, movement, and interaction in a 3D space. To create a truly immersive experience, designers must ensure that the technology is easy to use and that the user’s journey is intuitive.
As VR and AR continue to develop and become more mainstream, UX designers must adapt their approach to ensure that these cutting-edge technologies are accessible to everyone. It’s essential to keep in mind that the success of VR and AR products relies heavily on the user’s ability to engage with the technology and enjoy the experience.
Service design
In the world of UX design, it’s not just about creating tangible objects and digital products; it’s also about designing experiences. That’s where service design comes in.
Service design is the process of planning and organizing the people, infrastructure, communication, and material components of a service to improve its quality and the interaction between the service provider and its customers. It can be used to improve an existing service or create a completely new one.
When you buy a cup of coffee, stay in a hotel, or use public transportation, your experience is the result of service design. The service design methodology is quite similar to classic UX design, as both aim to create a positive experience for the end-user.
Service design involves looking at the entire customer journey, from start to finish, and ensuring that every touchpoint is designed with the user in mind. This means understanding the needs and wants of the user, as well as the business goals of the service provider.
By considering all of these factors, service designers can create seamless, enjoyable experiences that meet the needs of both the customer and the business.
Customer retention
As the business world becomes more and more customer-centric, customer retention has become a crucial goal for companies. User experience (UX) designers have a unique role to play in achieving this goal. With their specific data sets, UX designers can pinpoint areas that need improvement and help retain customers by reducing friction points in the user journey.
There are several areas where UX designers can have a significant impact on customer retention:
- App design
- Product design
Lead Generation
Lead generation is a crucial aspect of any business, and incorporating a UX designer’s expertise can give your generation machine the best chance possible at success. UX designers can provide valuable qualitative input and guidance or even design a lead gen flow that is tailored to your business needs.
One of the most important things UX designers can do is to ensure that the lead generation process is easy and intuitive for the user. This includes:
- optimizing the user journey
- minimizing form fields
- making sure that the call-to-action is clear and prominent
In addition to optimizing the lead generation process, UX designers can also ensure that the lead gen form is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This involves designing with accessibility in mind and testing the form for usability and compatibility with assistive technologies.
Internal processes and systems
As businesses grow, so does the need for effective internal processes and systems. This is where UX designers can provide valuable input, not only in terms of enhancing customer experience but also in improving internal processes and systems that can lead to employee satisfaction and retention.
UX designers can apply their expertise to develop strategies that support internal processes and systems, such as designing effective communication methods or creating intuitive software interfaces that make employee tasks easier and more efficient.
By utilizing a combination of hard and soft skills, user experience designers can provide guidance, support, and technical solutions for developing new systems and processes that are effective and user-friendly.
UX design disciplines: The quadrant model
UX design has grown to become a vast and multifaceted field that encompasses a range of disciplines. To better understand the different facets of UX, practitioners have developed various models to help classify and categorize its various disciplines.
One such model is the quadrant model, which divides UX into four main disciplines: Experience Strategy (ExS), Interaction Design (IxD), User Research (UR), and Information Architecture (IA).
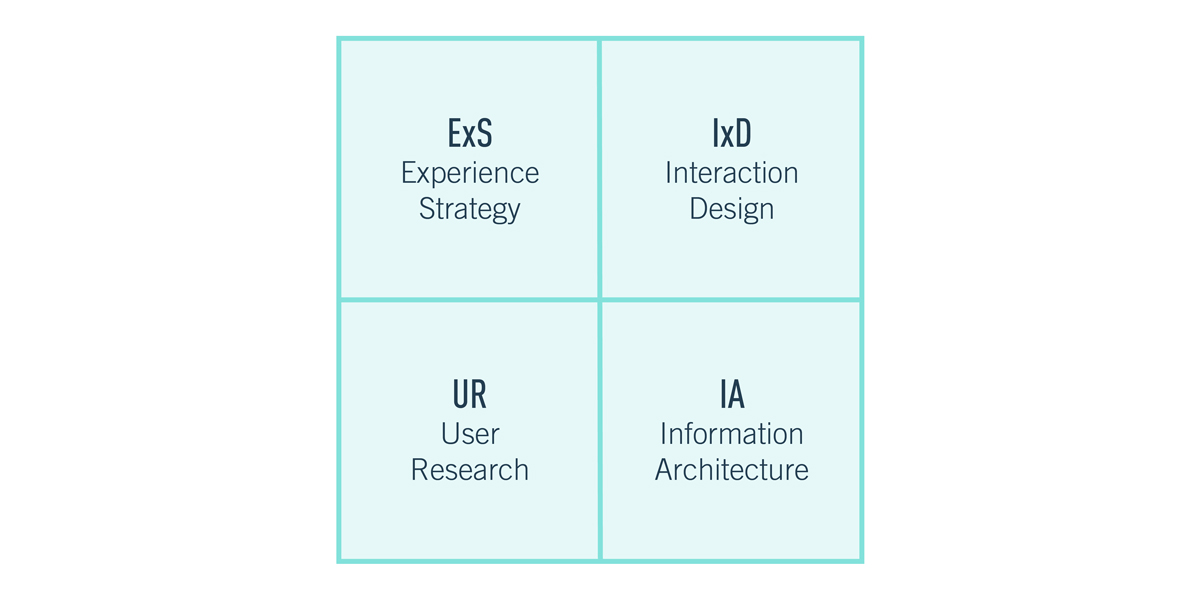
UX Design Disciplines: The Quadrant Model
Experience Strategy (ExS)
Experience Strategy (ExS) is an essential part of user experience design that goes beyond just catering to the end user. It takes into account the broader business objectives and creates a holistic strategy that aligns with both the customer’s needs and those of the company.
This means that UX designers must be well-versed in business strategy and work collaboratively with other stakeholders to ensure that the product or service being offered is not only user-friendly but also meets the company’s goals.
Interaction Design (IxD)
Interaction design is a critical component of UX design that focuses on designing interactions between users and digital systems. This discipline involves creating intuitive designs that enable users to perform core tasks and actions effortlessly.
To achieve this goal, interaction designers consider all interactive elements such as buttons, page transitions, and animations, among others.
In today’s world, where user attention spans are limited and competition is intense, creating delightful and seamless user experiences is crucial. Interaction design plays a vital role in achieving this by making digital systems more user-friendly and intuitive.
User Research (UR)
At the core of UX design is the process of identifying a problem and designing a solution that meets the needs of the end user. This requires a deep understanding of the user’s needs and objectives, which is where user research comes in.
During the research phase, UX designers will launch surveys, conduct interviews, and usability testing, and create user personas to gain insights into the end user’s behaviour, motivations, and pain points. By gathering both qualitative and quantitative data, UX designers can make informed design decisions that align with the user’s needs and preferences.
But user research isn’t a one-time activity. It’s an ongoing process that helps designers stay up-to-date with evolving user needs and preferences. By continuously gathering and analyzing data, UX designers can iterate and improve their designs to deliver better experiences.
Information Architecture (IA)
Information architecture (IA) is an essential aspect of user experience design, encompassing the practice of organizing information and content in a way that makes it accessible and meaningful for users. The goal of IA is to help users navigate around a product and find the information they need quickly and easily.
To determine the IA of any given product, information architects consider the relationship between different sets of content, paying close attention to language and ensuring that it is both convincing and consistent. This requires a deep understanding of the user’s needs and objectives, as well as an understanding of the product and its intended use.
Each of these areas requires a unique skill set and approach to ensure a successful user experience. UX design is a multidisciplinary field that draws upon elements of cognitive science and psychology, computer science, communication design, usability engineering, and more.
By understanding and mastering these disciplines, UX designers can create products that not only meet the needs of their users but also provide value to the business providing the product or service. It’s important to remember that UX design is not just about the end user, but also about devising a holistic business strategy that incorporates both the customer’s needs and those of the company.
The value of UX design
The benefits of UX design are numerous, and they extend beyond just creating a better user experience. Here are some of the key benefits that UX design can provide:
- Improved User Satisfaction: The most obvious benefit of UX design is that it creates a better user experience. When users can easily navigate and use a product, they are more likely to be satisfied with it. This satisfaction can lead to increased loyalty and repeat business.
- Increased Engagement: When a product has a good user experience, users are more likely to engage with it. This can lead to increased usage and adoption rates.
- Reduced Costs: UX design can also help reduce costs by reducing the amount of time and resources needed to develop a product. By understanding user needs and requirements upfront, designers can avoid costly redesigns and iterations later in the development process.
- Increased Revenue: Good UX design can also lead to increased revenue. When users are satisfied with a product, they are more likely to recommend it to others, leading to increased sales.
- Competitive Advantage: In today’s crowded marketplace, having a good user experience can provide a competitive advantage. Companies that invest in UX design are more likely to stand out from their competitors and attract and retain customers.
- Better Brand Image: A good user experience can also improve a company’s brand image. When users have a positive experience with a product, they are more likely to have positive feelings about the company as a whole.
- Improved Accessibility: Finally, UX design can improve accessibility for users with disabilities. By designing with accessibility in mind, designers can ensure that their products are usable by a wider range of users.
UX design can provide numerous benefits to both users and businesses. By creating a better user experience, companies can improve customer satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty, while also reducing costs and increasing revenue.
How UX design works
UX design is a process-driven approach that is based on research, prototyping, testing, and iteration. The process involves working closely with stakeholders, including developers, product managers, and users, to ensure that the final product is designed to meet the needs of everyone involved.
Here’s a breakdown of the typical UX design process:
1. Research
In the research stage, UX designers aim to gather as much information as possible about the target users and their needs. This involves conducting user interviews, surveys, and observing user behaviour. By doing so, designers can understand the motivations and behaviours of users, as well as the problems they’re trying to solve.
2. Analysis
After gathering data, UX designers analyze the information to identify key insights and user pain points. They may use tools such as user personas or empathy maps to develop a deep understanding of the target audience. This analysis helps designers to develop a design strategy that addresses the user’s needs effectively.
3. Ideation
In the ideation stage, designers use the insights gathered from the analysis stage to brainstorm potential solutions. This may involve sketching, wireframing, or creating prototypes to test out ideas. The goal of this stage is to explore different design solutions and determine the best approach to solve the user’s problems.
4. Design
Once a design strategy has been developed, designers move on to creating detailed visual designs and user interfaces. They consider things such as typography, colour, and layout, and ensure that the design aligns with the project’s goals and the user’s needs.
5. Testing
In the testing stage, UX designers conduct usability testing to evaluate the effectiveness of their designs. They observe how users interact with the product and identify any issues or areas for improvement. This feedback is then used to refine the design and make adjustments before launching the final product.
6. Launch
Finally, the product is launched, and UX designers continue to gather feedback from users. This helps them to identify any issues or areas for improvement that were missed during the testing stage. This feedback is then used to make updates to the product and improve the user experience.
The goal of UX design is to create products and experiences that are user-centred, intuitive, and effective. By focusing on the needs and behaviours of the user, designers can create products that not only meet the user’s needs but also drive business value by increasing engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty.
Enhance Your Growth with a UX Design Strategy
To truly propel your business growth and success, consider incorporating a UX design strategy that places user needs at the forefront of design decisions. By doing so, you’ll improve customer satisfaction, increase conversions, and boost revenue, all essential factors for a thriving business.
Prioritizing user experience can lead to increased user satisfaction, higher conversion rates, and improved brand loyalty. In essence, focusing on UX design gives you a competitive advantage and positions you as an industry leader among your competitors.
Furthermore, investing in UX design keeps you competitive in an ever-changing market, ensuring that you consistently provide a superior user experience. So, if you’re looking to elevate your business, think about including UX design in your strategy as a customer-centric approach.
Are you ready to transform your business for growth and success? Take your business to the next level with the help of The Brand Shop. Let us work together to create an exceptional UX design that will set you apart from the competition.
Reach out to us today and begin your journey to improved growth and customer satisfaction!




